Warning that COVID-19 has been linked to a host of potentially long-term health effects, Los Angeles County’s chief medical officer said Thursday people shouldn’t be fooled into thinking the illness is a “simple disease” with minimal impacts on the bulk of its victims.
“Any and all notions that COVID-19 is a relatively simple disease in which a small percentage of persons suffer severe consequences and the rest quickly recover must be dismissed,” Dr. Jeffrey Gunzenhauser told reporters during an online media briefing. “This simply is not the case. What we are seeing is that this is an infection that affects health in many ways, including what appear to be many long-term health consequences.”
Gunzenhauser walked through a litany of health issues that have been linked to the coronavirus, while noting that studies are continuing, and experts are still learning about how the virus can have an impact on a variety of bodily functions.
“What we do know already is that COVID-19 can have a wide range of effects on various body systems, and that some of these health consequences can linger at least for months,” he said. “For example, you all know that the primary known feature of COVID-19 is that it can cause a pneumonia that can be serious. The type of pneumonia often associated with COVID-19 can cause longstanding damage to the tiny air sacks in the lungs. … Resulting scar tissue can lead in some individuals to long-term breathing problems, and we’re really just beginning to learn more about this.”
He said the virus has also been linked to problems in the circulatory system, including blood clots that can potentially lead to a stroke and have an impact on organs such as the lungs, liver and kidneys. It can also affect neurological systems and cause heart conditions, including inflammation and damage to “the heart muscle itself,” and inflammation of the covering around the heart.
“Imaging tests taken months after recovery from COVID-19 have shown lasting damage to the heart muscle, even in people who appear to have only mild symptoms,” Gunzenhauser said. “So we don’t really understand the long-term implications of these findings on these image studies, but it is possible these could result in increased risk of heart failure or other heart complications in the future.”
Gunzenhauser also said the suggestion that people who contract COVID- 19 and recover will forever be immune to it is unproven.
“This is not like other viral diseases where you have a short-term effect, a small group may be severely affected and the vast majority of others are good to go,” he said. “That’s not the case. That’s not what we’re seeing with COVID.”
He said the virus is similar to SARS, which arose in roughly 2003, and people who survived that malady later developed chronic fatigue syndrome.
“That’s why we continue to deliver the very simple message that it’s everyone’s personal responsibility to use the tools that we have available to us to slow the spread of COVID-19 and to prevent all of the harmful and severe consequences that this virus can cause, including the ones that can occur over a long period of years,” Gunzenhauser said.
His warnings came on a day that saw another upward spike in daily coronavirus case numbers in the county. The Department of Public Health reported 1,745 new coronavirus cases on Thursday, the highest single-day number since late August that did not involve a backlog in testing results.
Health officials said this week that the county’s average daily number of new cases has been on the rise all month, going from an average of about 940 per day in early October to nearly 1,200 in recent days.
That increase is sinking the county further into the mud of the most restrictive “purple” tier in the state’s coronavirus economic-reopening matrix. Until the daily case numbers drop to a steady average of about 700 per day, the county will be unable to substantially lift business restrictions or allow school campuses to reopen.
The new cases reported by the county, along with 37 announced by Long Beach health officials and 18 by Pasadena, lifted the countywide cumulative total since the start of the pandemic to 305,125.
Los Angeles County also announced another 19 coronavirus-related deaths, lifting the death toll to 7,044. There were 750 people hospitalized as of Thursday, down slightly from 755 on Wednesday.
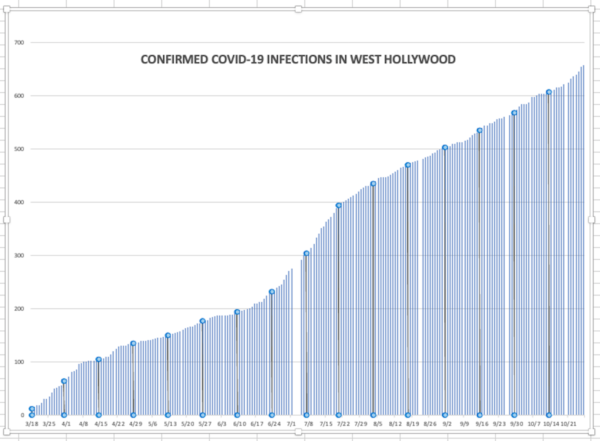
The number of infections among West Hollywood residents as of today has increased by four to 658. The number of people in West Hollywood who have died of COVID-19 related illnesses is still listed as five.
In Beverly Hills, the number of confirmed infections increased by one to 753. The number of COVID-19 related deaths in Beverly Hills to date 12. The number of COVID-19 infections confirmed among Culver City has increased by one to 426. The number of deaths to date is 28. The number of infections in Hollywood has increased by five to 1,404. The number of deaths to date remains at 15. The Melrose neighborhood’s number of infections has increased by ten to 2,155. The number of COVID-19 related deaths remains at 75.
Public Health has a dedicated call line for confirmed cases of COVID-19. If you are positive for COVID-19 and have not yet connected with a public health specialist or need more information on services, call toll-free at 1 (833) 540-0473. Residents who do not have COVID-19 can continue to call 211 for resources or more information.
One way the virus can be transmitted is through a cough, a sneeze or even through air that comes from the mouth when someone talks. For that reason, residents must wear face coverings when out in public and can be cited for not doing so. The citations come with a $250 fine and a $50 administrative fee.
West Hollywood residents with questions about the COVID-19 pandemic or who are looking for resources to deal with it can find answers on the City of West Hollywood’s website. Here is a list of links to sections about particular subjects and issues:
